Single Conductor Coaxial Cables feature a central conductor surrounded by insulating material and a metallic shield, ensuring efficient transmission of signals with minimal interference. Widely used in telecommunications, broadcasting, and data transmission, they offer reliable performance for various applications requiring high-quality signal transmission.
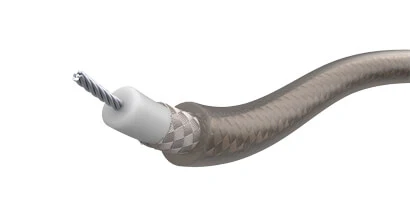
Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1400V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 750V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 750V
Insulation: FEP / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17
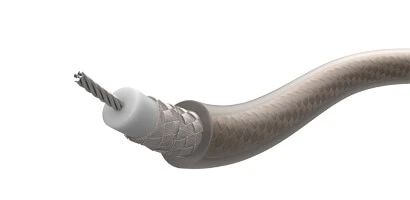
Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 900V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +150°C
Operating Voltage: 900V
Insulation: FEP / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 900V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 900V
Insulation: FEP / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1400V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1700V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1400V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 3000V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1200V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +150°C
Operating Voltage: 1200V
Insulation: FEP / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1200V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1200V
Insulation: FEP / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17

Operating Temperature: -55°C to +200°C
Operating Voltage: 1200V
Insulation: PTFE / FEP
Approval: Meets MIL-DTL-17
1. Central Conductor:
Single Core: The cable consists of a single central conductor, typically made of copper or another conductive material. This conductor carries the signal through the cable.
Solid or Stranded: The central conductor may be solid (single piece) or stranded (multiple small wires twisted together), providing flexibility and durability.
2. Dielectric Insulation:
Insulating Material: Surrounds the central conductor to provide electrical insulation and maintain the integrity of the signal.
Low-Loss Dielectric: The dielectric material (e.g., polyethylene, foam polyethylene, PTFE) minimizes signal attenuation and maintains impedance characteristics across a range of frequencies.
3. Shielding:
Shielding Layer: Surrounds the dielectric insulation to protect the signal from external interference and reduce electromagnetic radiation.
Types of Shielding: Common shielding options include:
Foil Shield: Thin metallic foil wrapped around the dielectric.
Braided Shield: Interwoven strands of metallic wire (e.g., copper or aluminum) providing higher flexibility and enhanced shielding effectiveness.
4. Impedance Matching:
Consistent Impedance: Maintains a specified characteristic impedance (e.g., 50 ohms or 75 ohms) along the length of the cable for efficient signal transmission and minimal signal reflection.
5. High-Frequency Performance:
Designed for High Frequencies: Supports high-frequency signals, making them suitable for telecommunications, RF applications, and data transmission.
6. Flexible and Lightweight:
Flexibility: Flexible design allows for easy installation and routing in confined spaces.
Lightweight Construction: Suitable for portable equipment and applications where weight is a concern.
7. Temperature and Environmental Resistance:
Wide Temperature Range: Capable of operating over a range of temperatures, making them suitable for indoor and outdoor applications.
Environmental Resilience: Resistant to moisture, chemicals, and other environmental factors to ensure reliable performance in various conditions.
8. Customizable Options:
Variety of Sizes and Configurations: Available in different sizes (gauges) and configurations to suit specific application requirements.
Connector Compatibility: Compatible with a wide range of connectors for easy integration into systems and equipment.
9. Application-Specific Variants:
Specialized Versions: Some single conductor coaxial cables are designed for specific applications such as high-power transmission, low-loss applications, or extreme environmental conditions.
1. Telecommunications:
Data Transmission: Single conductor coaxial cables are used in telecommunications networks for transmitting high-speed data signals, including internet, voice, and video.
Cable Television (CATV): Used for distributing cable TV signals from broadcasting stations to homes and businesses.
2. Broadcasting and Audio/Video Equipment:
Television Broadcasting: Single conductor coaxial cables are employed in broadcasting stations for transmitting television signals from production studios to transmission towers.
Audio/Video Production: Used in professional audio/video equipment for signal distribution and transmission, ensuring high-quality audio and video signals.
3. RF (Radio Frequency) and Microwave Applications:
RF Testing Equipment: Utilized in RF testing and measurement applications, including spectrum analyzers, signal generators, and RF testing chambers.
Microwave Links: Single conductor coaxial cables are used in microwave communication systems for point-to-point and point-to-multipoint transmission of high-frequency signals.
4. Instrumentation and Measurement:
Scientific Instruments: Employed in laboratory instrumentation for measuring and analyzing signals in research and development environments.
Industrial Control Systems: Used in industrial automation and control systems for transmitting signals between sensors, actuators, and control devices.
5. Aerospace and Defense:
Military Communication Systems: Single conductor coaxial cables are critical components in military communication systems, radar systems, and electronic warfare equipment.
Aerospace Applications: Used in aircraft and spacecraft for avionics systems, navigation equipment, and onboard communication.
6. Medical Devices:
Medical Imaging Equipment: Single conductor coaxial cables are used in MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines, CT (Computed Tomography) scanners, and other medical imaging devices for signal transmission.
RF Therapy Devices: Employed in medical devices for radiofrequency (RF) therapy and treatment applications.
7. Test and Measurement Equipment:
Test Probes and Test Leads: Used in electronic test equipment for connecting and testing circuits and components.
8. Industrial and Manufacturing:
Process Control Systems: Employed in industrial control systems, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems for monitoring and controlling manufacturing processes.
9. Research and Development:
Laboratory Equipment: Used in research and development laboratories for experimental setups, signal analysis, and data acquisition.